 |
| January 22, 2019 | Volume 15 Issue 03 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Army gives details on munitions that go further, much faster
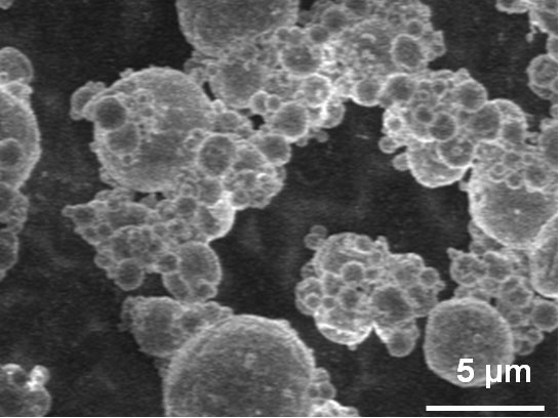
This scanning electron micrograph shows the pristine aluminum (Al) particles.
Researchers from the U.S. Army and top universities have discovered a new way to get more energy out of energetic materials containing aluminum, common in battlefield systems, by igniting aluminum micron powders coated with graphene oxide.
This discovery coincides with one of the Army's modernization priorities: Long Range Precision Fires. This research could lead to enhanced energetic performance of metal powders as propellant/explosive ingredients in Army munitions.
Lauded as a miracle material, graphene is considered the strongest and lightest material in the world. It's also the most conductive and transparent, and expensive to produce. Its applications are many, extending to electronics by enabling touchscreen laptops, for example, with light-emitting diode (LED) or organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays, and medicine like DNA sequencing. By oxidizing, graphite is cheaper to produce en masse. The result: graphene oxide (GO).
Although GO is a popular two-dimensional material that has attracted intense interest across numerous disciplines and materials applications, this discovery exploits GO as an effective, light-weight additive for practical energetic applications using micron-size aluminum powders (ľAl), i.e., aluminum particles one-millionth of a meter in diameter.
The research team published their findings in the October edition of ACS Nano with collaboration from the RDECOM Research Laboratory, the Army's corporate research laboratory (ARL), Stanford University, University of Southern California, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Argonne National Laboratory.
This new published work signals a beginning at ARL for the development of functionalized particles as novel energetics under several new leveraged programs led by Drs. Chi-Chin Wu and Jennifer Gottfried. ARL is leading joint scientific efforts with the University of Tennessee, Texas Tech University, Army Research, Development and Engineering Center at Picatinny, NJ, and with the Air Force Research Laboratory establishing a new research avenue to develop superior novel metal propellant/explosive ingredients to protect more lives for the Army warfighters.
"Because aluminum (Al) can theoretically release a large quantity of heat (as much as 31 kilojoules per gram) and is relatively cheap due to its natural abundance, ľAl powders have been widely used in energetic applications," said Wu. However, they are very difficult to be ignited by an optical flash lamp due to poor light absorption. To improve the light absorption of ľAl during ignition, it is often mixed with heavy metallic oxides, which decrease the energetic performance," Wu said.
Nanometer-sized Al powders (i.e., one-billionth of a meter in diameter) can be ignited more easily by a wide-area optical flash lamp to release heat at a much faster rate than can be achieved using conventional single-point methods such as hotwire ignition. Unfortunately, nanometer-sized Al powders are very costly.
The team demonstrated the value of ľAl/GO composites as potential propellant/explosive ingredients through a collaborative research effort led by Professor Xiaolin Zheng at Stanford University and supported by ARL's Drs. Wu and Gottfried. This research demonstrated that GO can enable the efficient ignition of ľAl via an optical flash lamp, releasing more energy at a faster rate -- thus significantly improving the energetic performance of ľAl beyond that of the more expensive nanometer-sized Al powder. The team also discovered that the ignition and combustion of ľAl powders can be controlled by varying the GO content to achieve the desired energy output.
Images showing the structure of the ľAl/GO composite particles were obtained by high-resolution transmission electron (TEM) microscopy performed by Wu, a materials researcher who leads the plasma research for the Energetic Materials Science Branch in the Lethality Division of the Weapons and Materials Research Directorate at ARL. "It is exciting to see with our own eyes through advanced microscopy such as TEM how a simple mechanical mixing process can be used to nicely wrap the ľAl particles in a GO sheet," said Wu.
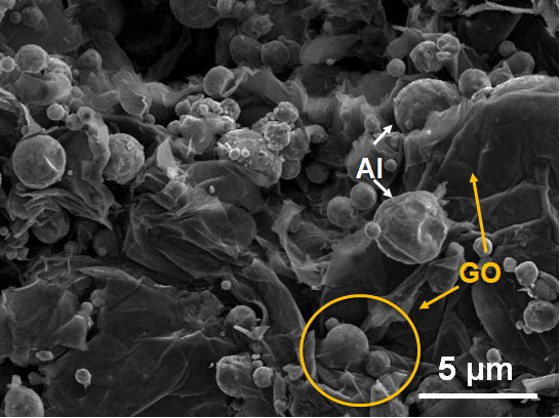

Scanning electron micrograph shows the Al/GO composite.
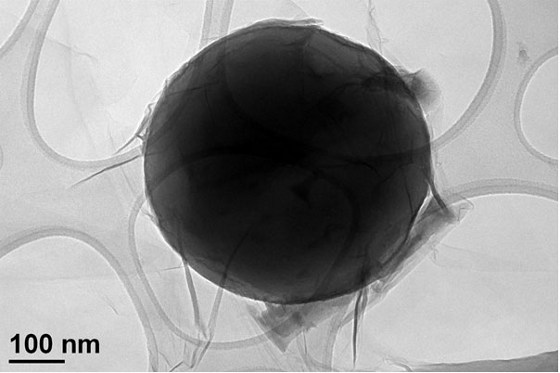
High-resolution transmission electron micrograph shows GO wrapping on a single Al particle.
In addition to demonstrating enhanced combustion effects from optical flash lamp heating of the ľAl/GO composites by the Stanford group, Gottfried, a physical scientist at ARL, demonstrated that the GO increased the amount of ľAl reacting on the microsecond timescale, i.e., one-millionth of a second -- a regime analogous to the release of explosive energy during a detonation event.
Upon initiation of the ľAl/GO composite with a pulsed laser using a technique called laser-induced air shock from energetic materials (LASEM), the exothermic reactions of the ľAl/GO accelerated the resulting laser-induced shock velocity beyond that of pure ľAl or pure GO. According to Gottfried, "The ľAl/GO composite thus has the potential to increase the explosive power of military formulations, in addition to enhancing the combustion or blast effects." As a result, this discovery could be used to improve the range and/or lethality of existing weapons systems.
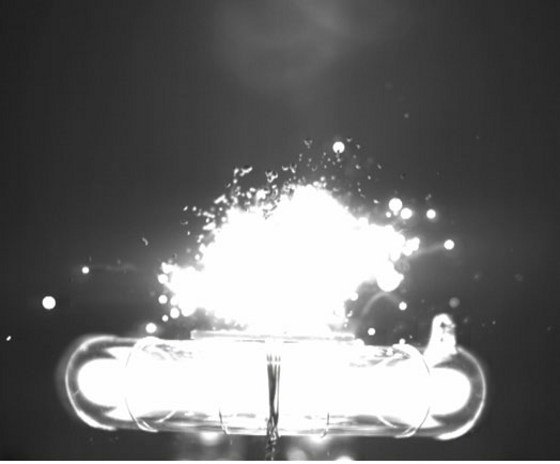
This image shows the composite being ignited by an optical flash lamp in air.
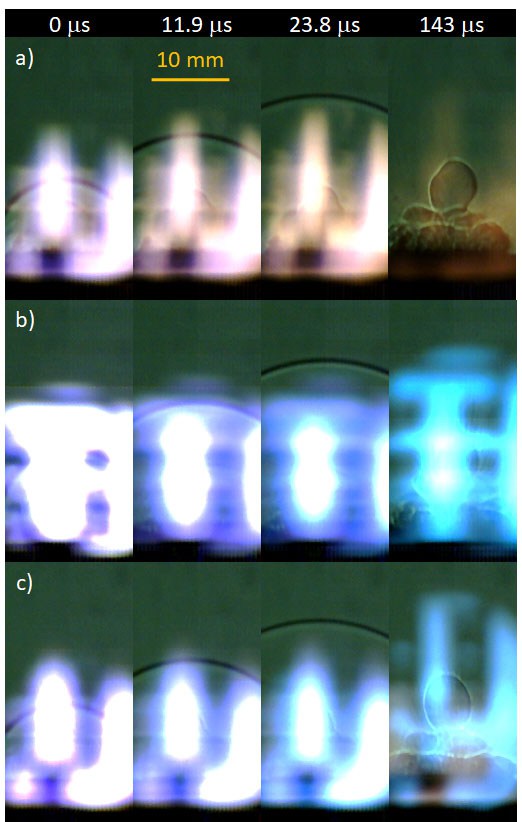
Schlieren images show shockwaves.
Details of this breakthrough work are described in the team's Oct. 15, 2018, published paper entitled "Energetic Performance of Optically Activated Aluminum/Graphene Oxide Composites" by Yue Jiang, Sili Dang, Sungwook Hong, Jiheng Zhao, Sidi Huang, Chi-Chin Wu, Jennifer L. Gottfried, Ken-ichi Nomura, Ying Li, Subodh Tiwari, Rajiv K. Kalia, Priya Vashishta, Aiichiro Nakano, and Xiaolin Zheng in the high-impact journal ACS Nano.
RELATED: In September 2018, a team of researchers from the U.S. Army Research Laboratory and Washington State University reported discovering a new type of energetic material that could have triple the energy content of well-known explosives. Simple components of air, such as nitrogen and carbon monoxide, can be transformed into high-energy polymeric solids when sufficient pressure and/or temperature is applied. See the Designfax article, "U.S. Army working on tripling energy of explosives."
Source: U.S. Army/RDECOM Research Laboratory
Published January 2019
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
